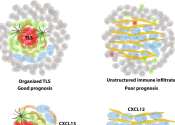
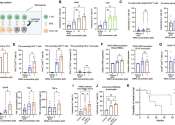
Researchers discover new therapeutic target for non-small cell lung cancer
Non-small cell lung cancer accounts for nearly 85% of all lung cancer cases. Targeted immunotherapy is a common treatment, but it does not work for everyone. However, a new Moffitt Cancer Center study published in the journal ...
17 hours ago
0
4