Treatment improved overall survival in elderly patients with early-stage esophageal cancer
Elderly patients with early-stage esophageal cancer that received treatment had an increased 5-year overall survival when compared to patients who received observation with no treatment.
Esophageal cancer is the eighth most common cancer worldwide and the sixth most common cause of death related to cancer. In the United States, there are over 16,000 people diagnosed with the disease annually with an even higher prevalence in other parts of the world. The National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) guidelines suggest surgery as the standard treatment for stage I esophageal cancer. Despite these guidelines, various factors prevent a patient from being managed surgically such as age of the patient, multiple comorbidities and differences in sociodemographic and socioeconomic status. The median age of patients diagnosed with esophageal cancer is around 67 years with a 5-year overall survival (OS) rate of 18.8%. Age often drives treatment decisions of elderly patients (? 80 years of age) representing a unique and challenging subpopulation to health care providers. Randomized clinical trials have shown that survival of patients with esophageal cancer correlates with the degree of treatment intensity they receive. However less aggressive, nonsurgical therapy such as chemoradiation is commonly provided to elderly patients even with early-stage disease.
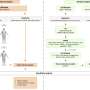
A group of researchers in the United States conducted a retrospective study to evaluate the practice patterns and outcomes of elderly patients (? 80 years of age) with stage I esophageal cancer who received four different types of treatment: esophagectomy (Eso), local excision (LE), chemoradiotherapy (CRT) and observation (Obs). The National Cancer Data Base (NCDB) was queried for patients ? 80 years of age diagnosed with cT1-T2 N0 esophageal cancer from 2004 to 2012. Patients meeting the criteria were divided into four groups: Eso, LE, CRT, and Obs. Patient, tumor, and treatment parameters were extracted and compared. Analyses were performed on OS and postoperative 30- and 90-day mortality.
The results of the study were published in the Journal of Thoracic Oncology, the official journal of the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer (IASLC). From the NCDB query, 923 patients were identified and analyzed. Of these, 43% were observed, 22% underwent CRT, 25% had LE and 10% had Eso. The median age was 84 years (range 80-90) for the overall cohort and lower in the Eso group compared to Obs (82 years vs. 85 years, p<0.001). Patients were predominantly male and Caucasian; however, the highest proportion of females and African Americans were found in the nonsurgical groups (Obs or CRT; p<0.001). Patients undergoing Obs were older, had more comorbidities, were treated at non-academic centers and lived ? 25 miles from the facility. Patients receiving surgery (Eso/LE) were more commonly younger, male, Caucasian and in the top income quartile. Five-year OS was 7% for Obs, 20% for CRT, 33% for LE and 45% for Eso. Postoperative 30-day mortality between the LE and Eso groups was 1.3% and 9.6% (p<0.001), which increased to 2.6% and 20.2% at 90 days. Multivariate analysis showed improved OS for all treatments when compared to Obs: CRT (HR: 0.42, 95% CI [0.34 - 0.52], p<0.001), LE (HR: 0.30, CI [0.24-0.38], p<0.001), Eso (HR: 0.32, CI [0.23-0.44], p<0.001).
The authors comment that, "In general, health disparities were observed in this study, which are important to characterize. When stratifying the elderly by any surgery vs. CRT/Obs, female patients, African Americans and patients of lower income quartile were less likely to undergo surgery - findings that corroborate the results from other retrospective studies in non-elderly cohorts. Another key factor that drives the treatment of choice and subsequent outcome is the type of treating facility. Although more than half of patients were treated within the community, 82% of these patients did not undergo surgery compared to 42% of patients treated in an academic center. A rather compelling finding was that patients living closer to treating institutions tended to undergo observation. This study demonstrated that a surprisingly large proportion of patients age ≥ 80 years with stage I esophageal cancer remain under clinical observation after their diagnosis. Any form of local therapy, including CRT, statistically improved OS when compared to observation. Finally, if surgery is feasible then LE should be considered over CRT and Eso, given the potentially lower toxicity profile and postoperative mortality rates."
More information: Amy C. Moreno et al, Patterns of Care and Treatment Outcomes of Elderly Patients With Stage I Esophageal Cancer: Analysis of the National Cancer Data Base, Journal of Thoracic Oncology (2017). DOI: 10.1016/j.jtho.2017.04.004